 Image 1 of 11
Image 1 of 11

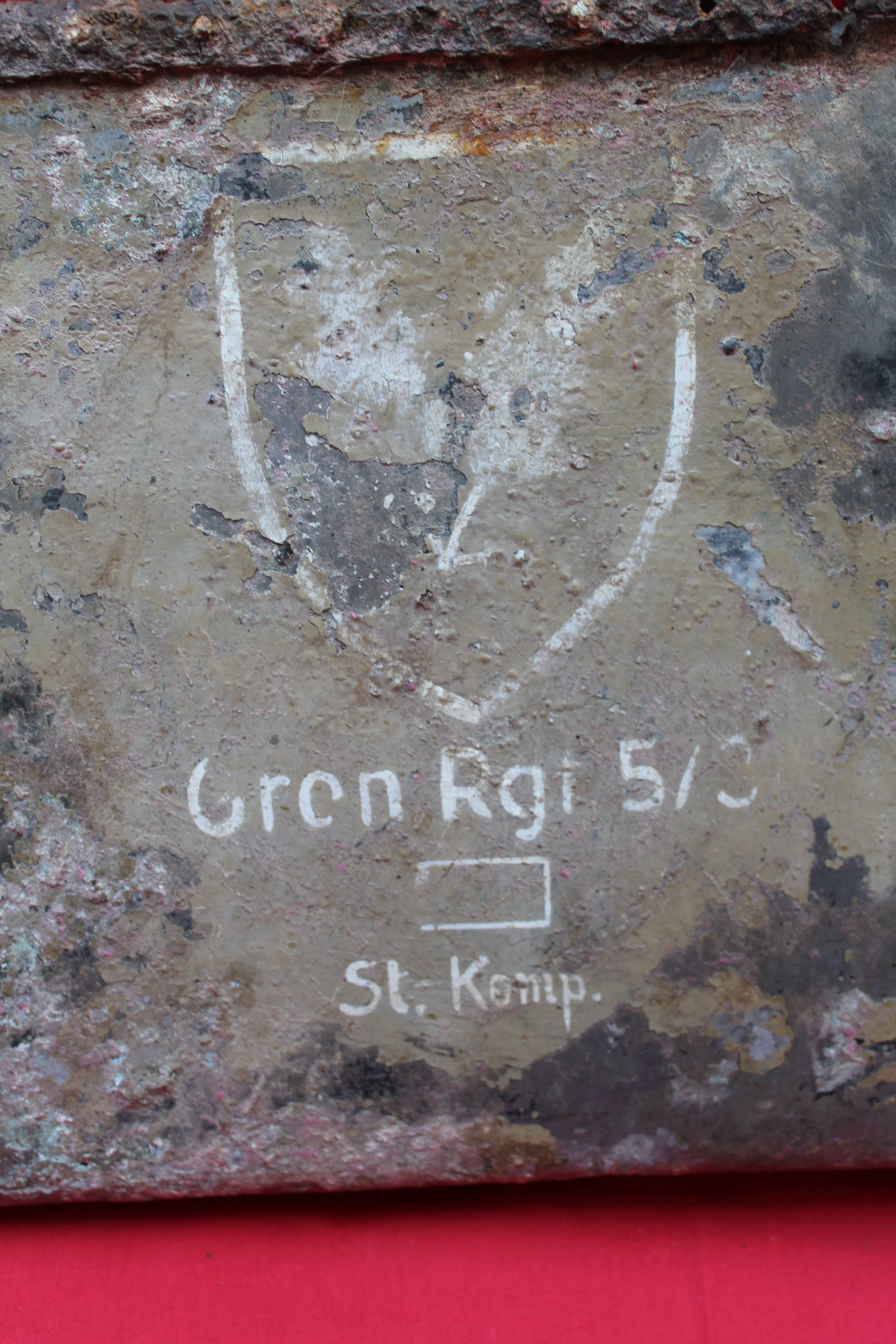 Image 2 of 11
Image 2 of 11
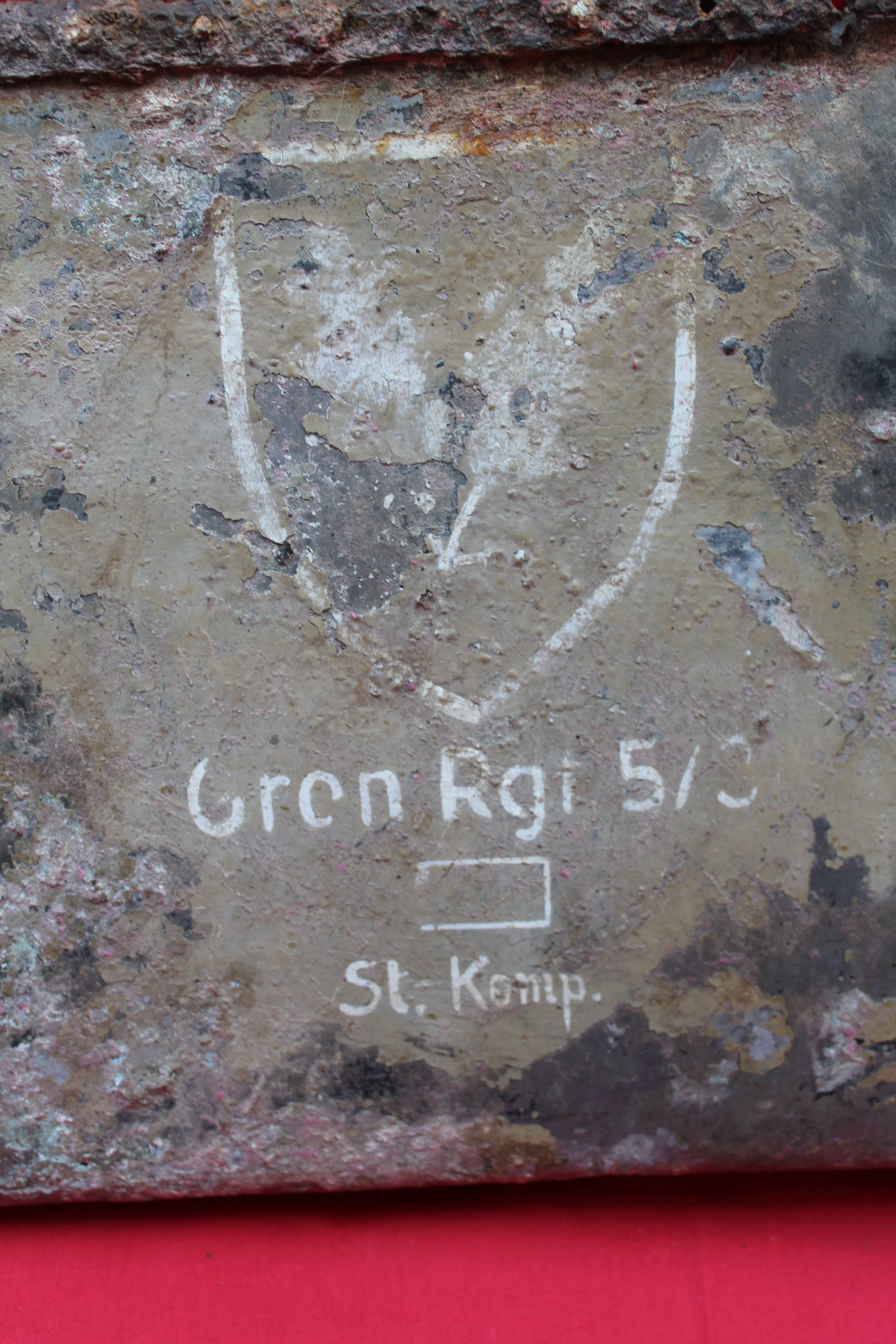
 Image 3 of 11
Image 3 of 11
 Image 4 of 11
Image 4 of 11
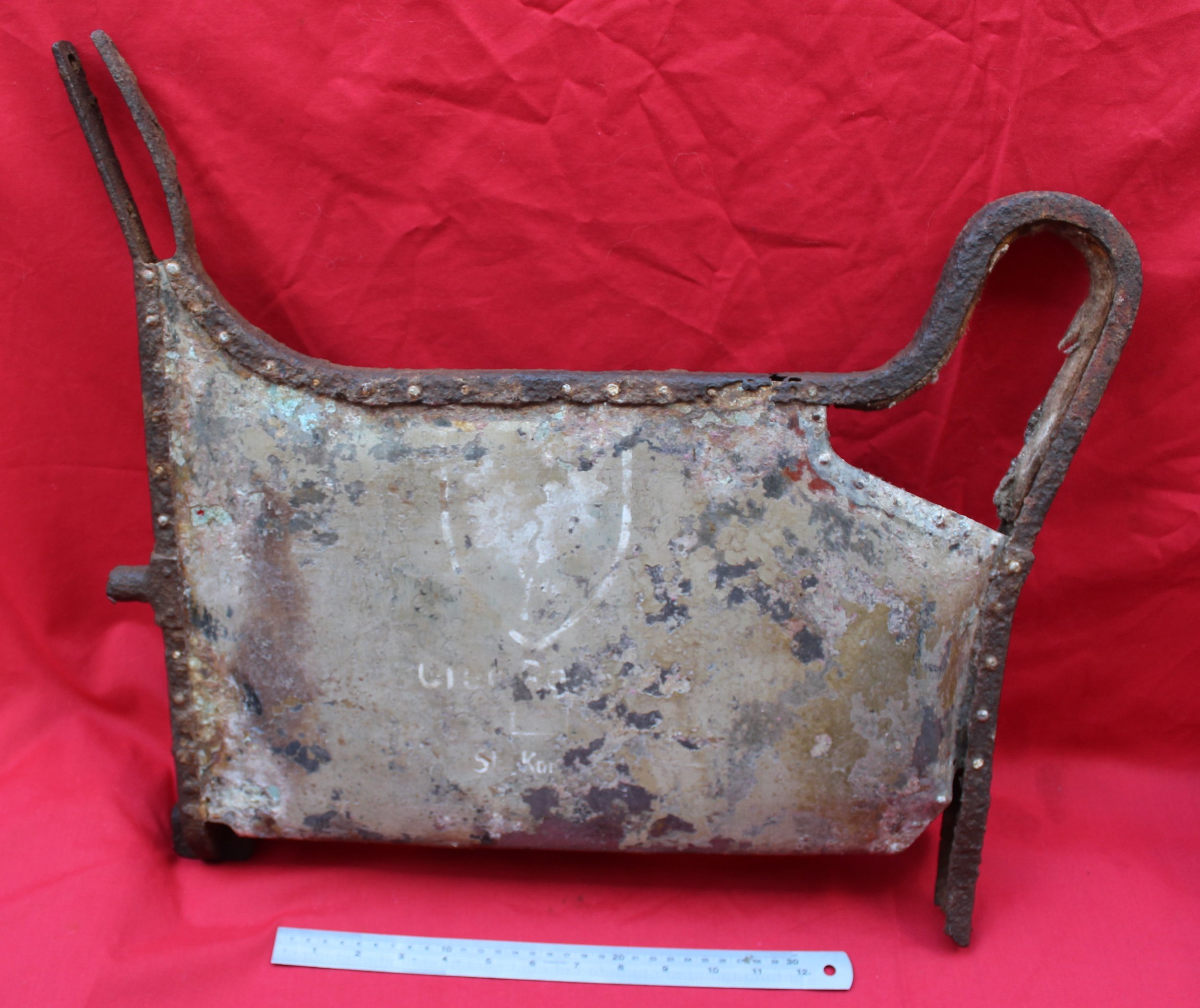
 Image 5 of 11
Image 5 of 11
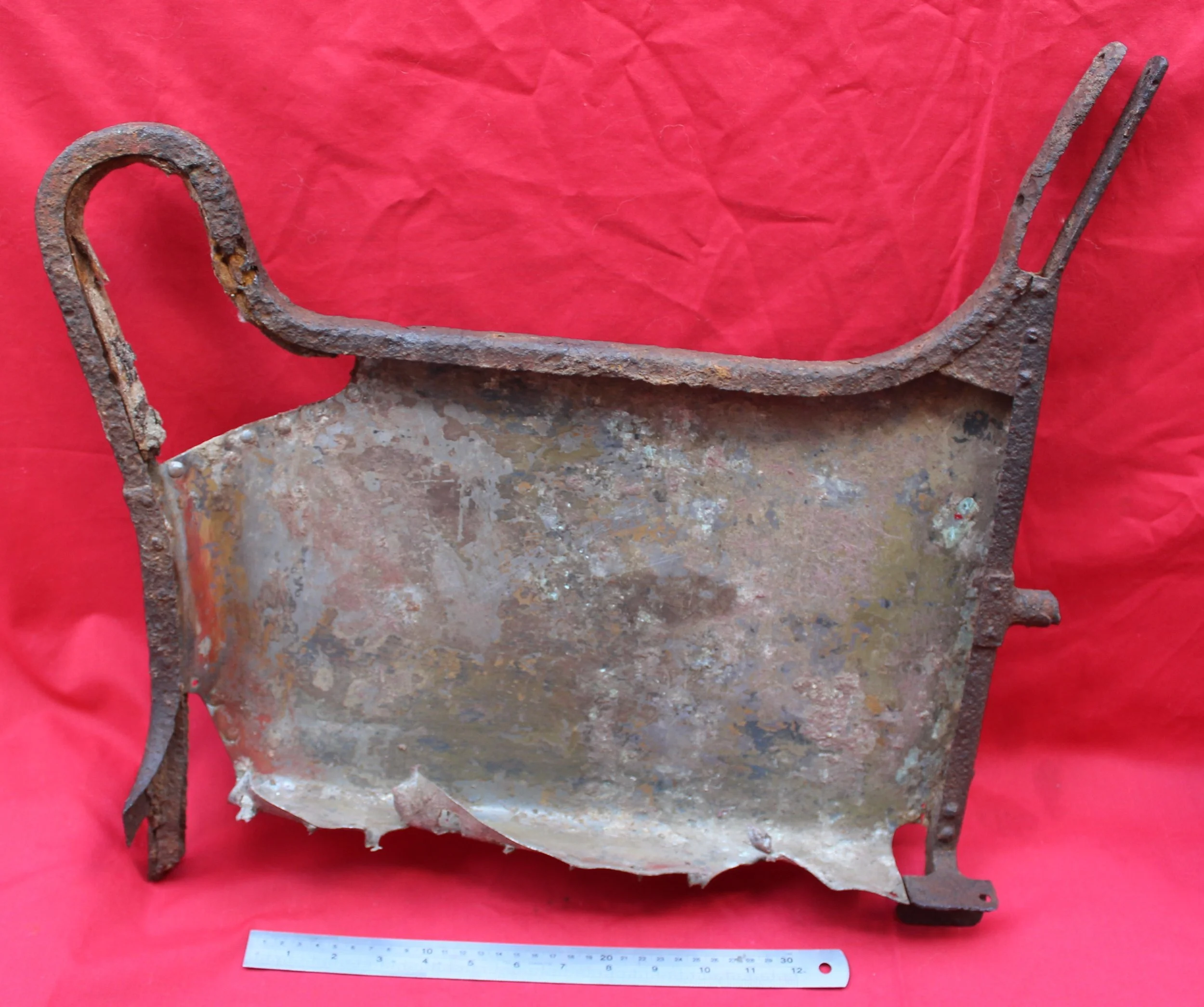
 Image 6 of 11
Image 6 of 11
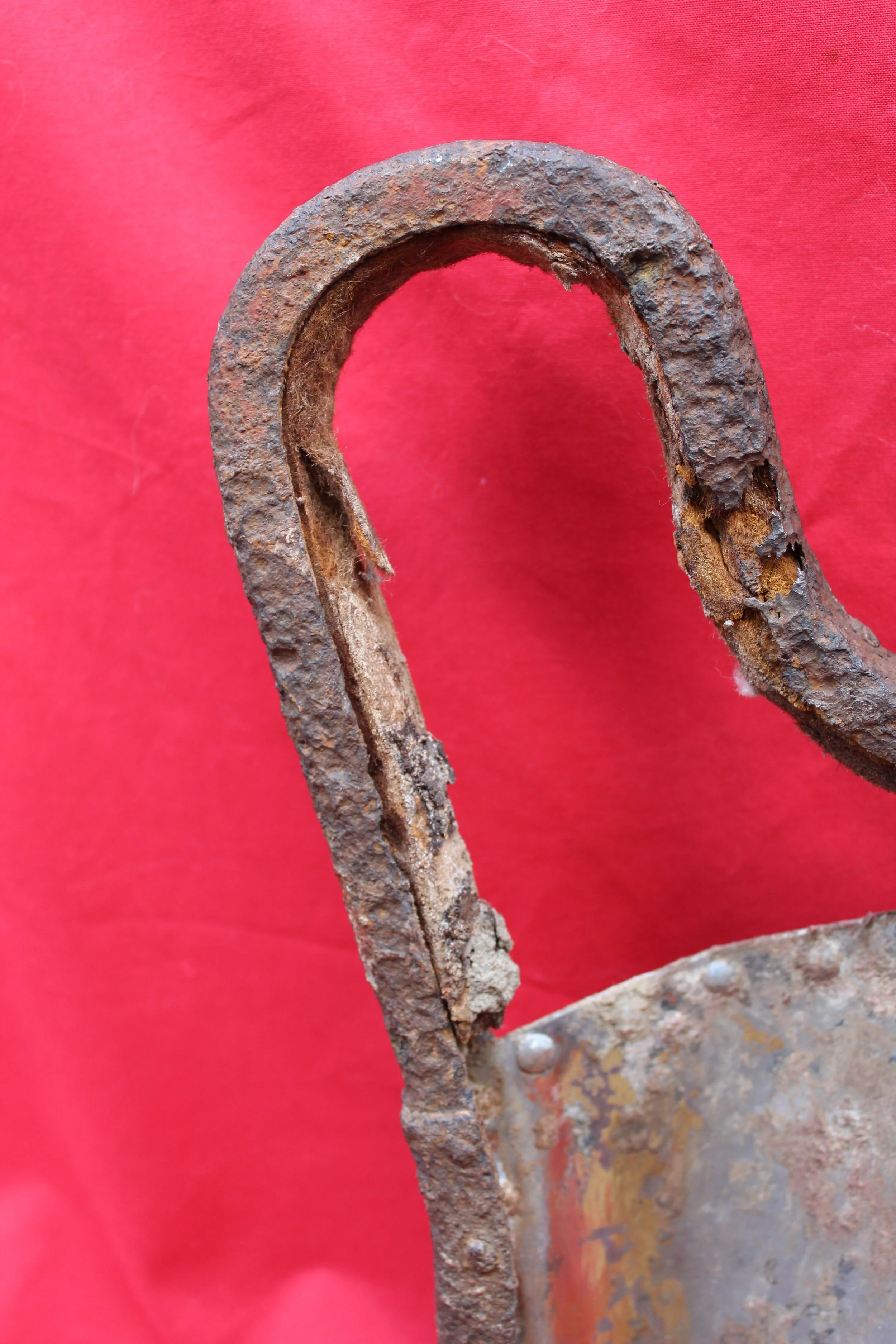
 Image 7 of 11
Image 7 of 11
 Image 8 of 11
Image 8 of 11
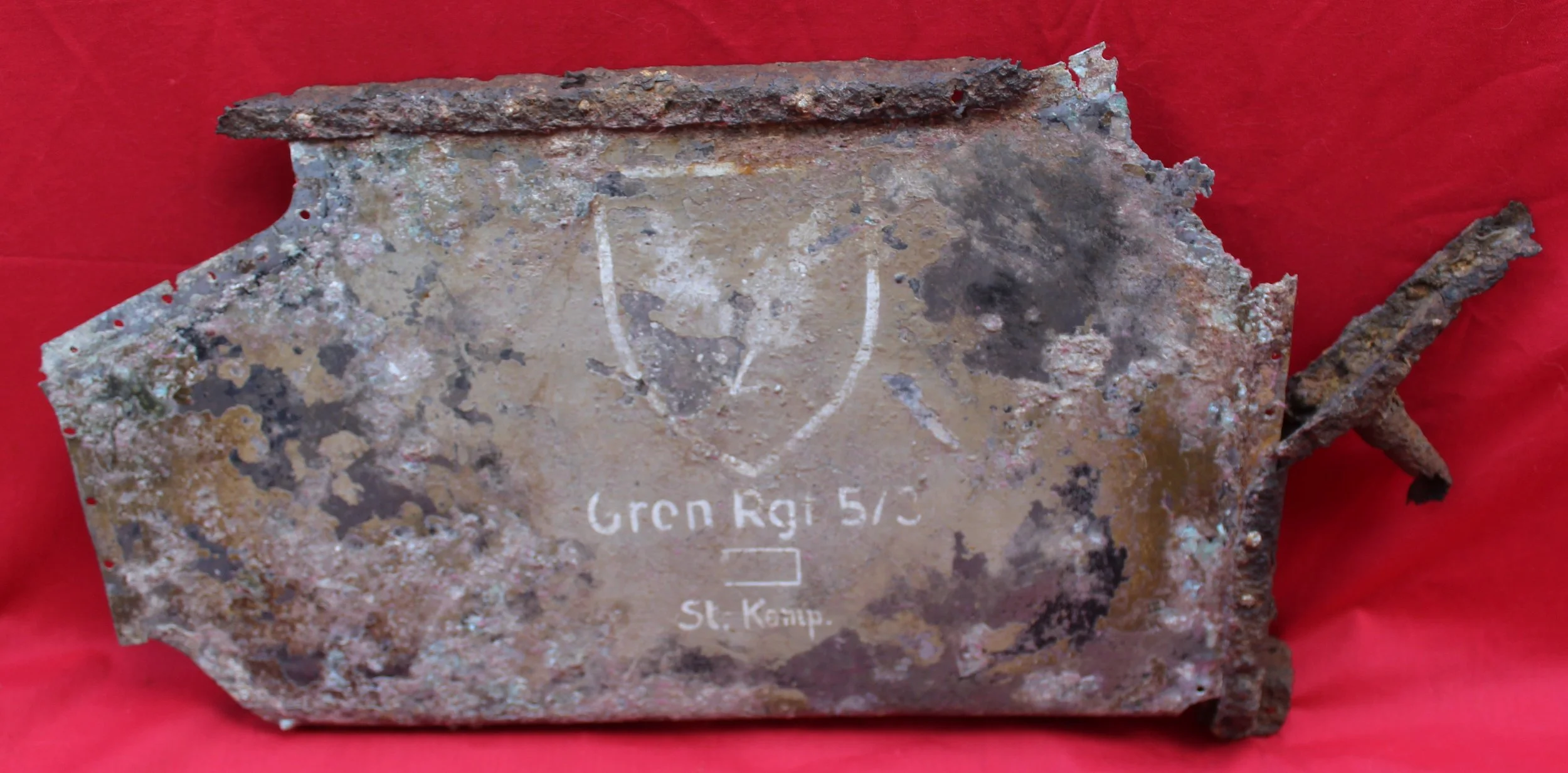
 Image 9 of 11
Image 9 of 11
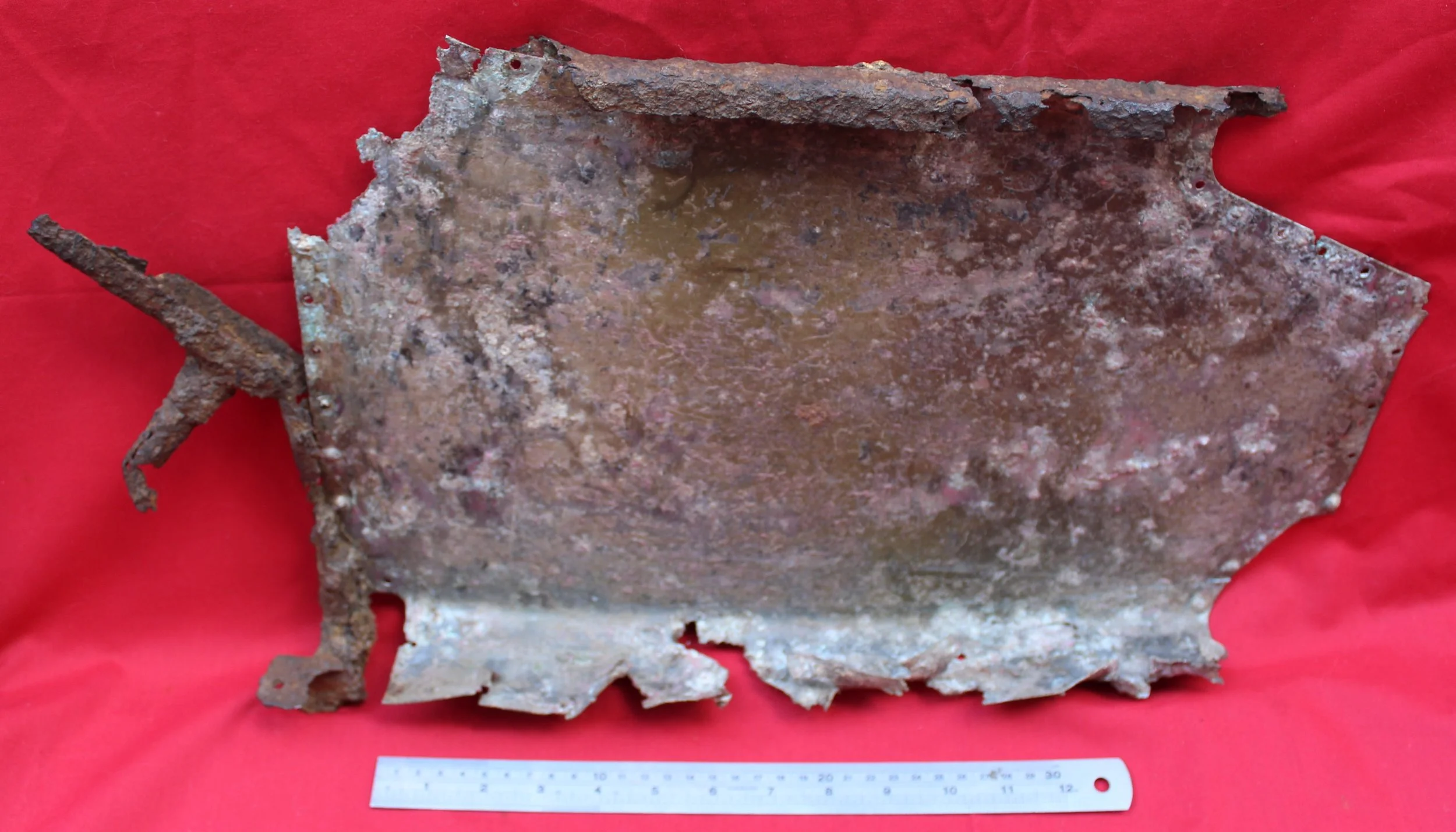
 Image 10 of 11
Image 10 of 11
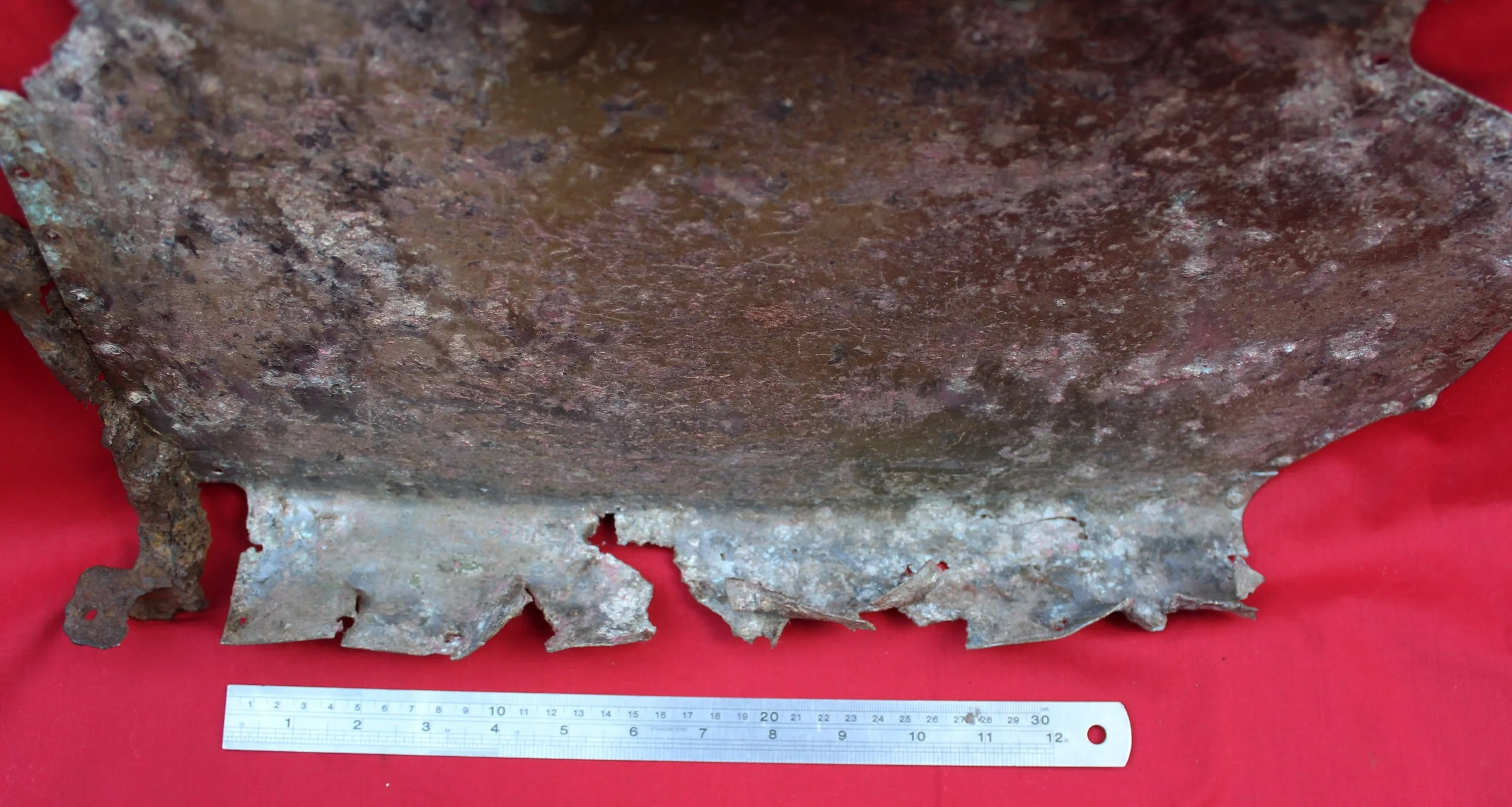
 Image 11 of 11
Image 11 of 11


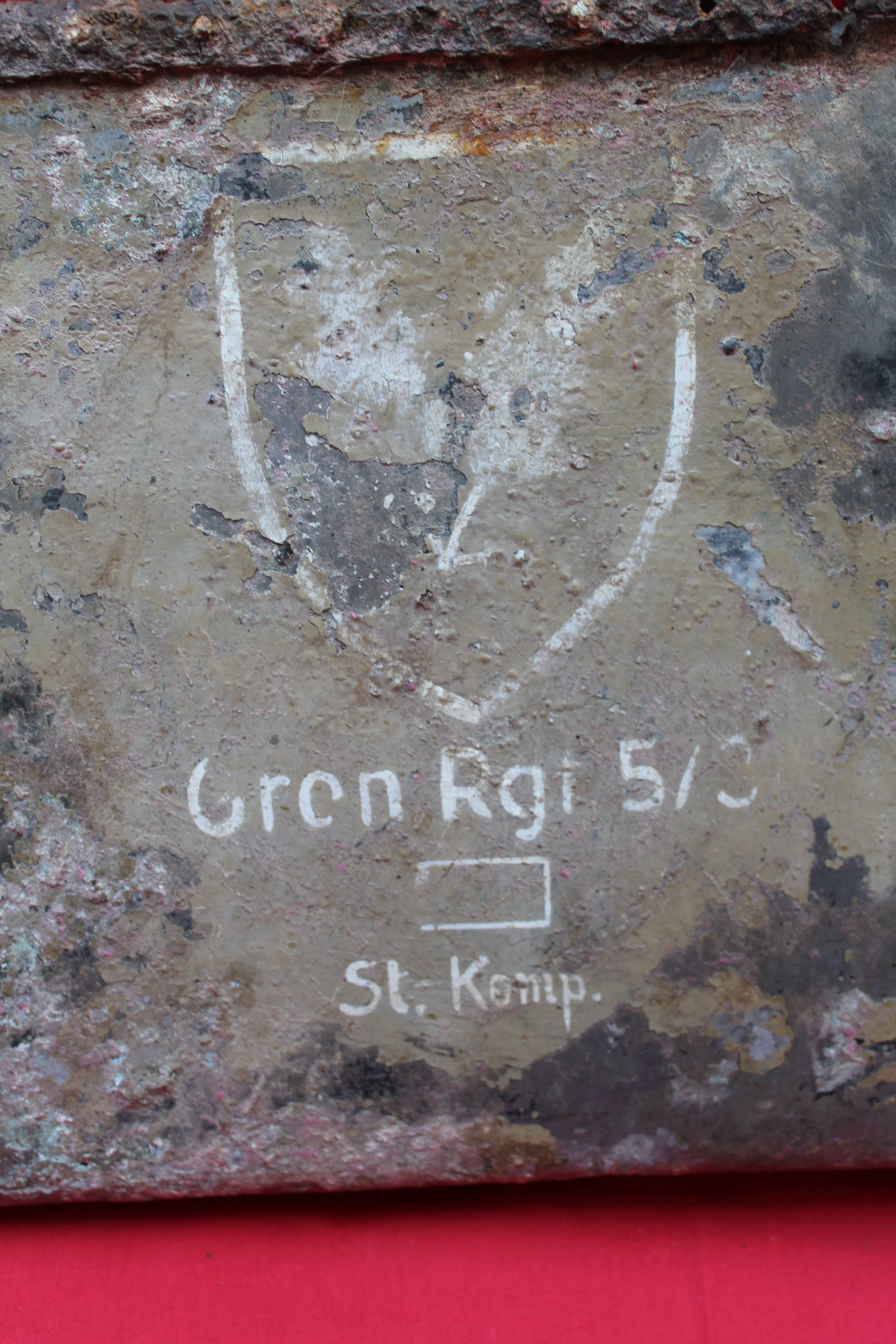









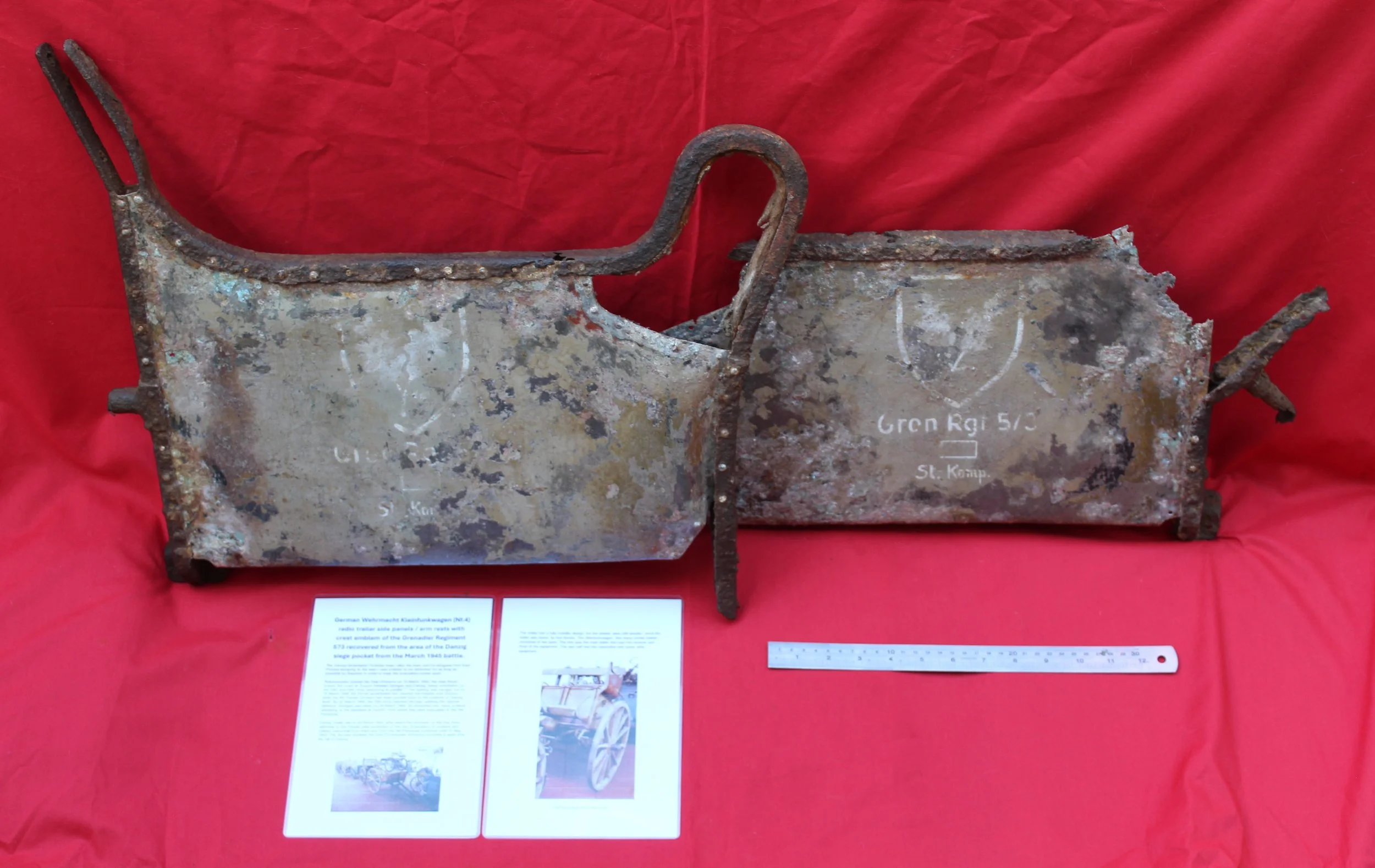
German Wehrmacht Kleinfunkwagen (Nf.4) radio trailer side panels / arm rests with crest emblem of the Grenadier Regiment 573 recovered from the area of the Danzig siege pocket from the March 1945 batt
£275.00
Only 1 available
Super rare relics with stunning original paintwork still visible! They have been lightly cleaned and treated with Renaissance wax to preserve their condition. Solid and well-preserved, these pieces make a fantastic addition to any collection.
The Danzig�Gotenhafen Fortified Area�also the main port for refugees fleeing East Prussia�was ordered to be defended as long as possible by Saucken to keep evacuation routes open.
Rokossovsky launched his final offensive on 15 March 1945, with the main thrust toward the coast at Zoppot, between Gdingen and Danzig, undertaken by the 70th and 49th Armies advancing in parallel. Fighting was intense, but by 19 March 1945, Soviet spearheads had reached the heights over Zoppot, while the 4th Panzer Division had been pushed back to the outskirts of Danzig itself. By 22 March, the 70th Army reached the sea, splitting the German defense. Gdingen fell on 26 March 1945, with defenders and many civilians retreating to the headland at Oxh�ft, from where they were evacuated to the Hel Peninsula.
Danzig finally fell on 30 March 1945. The remnants of the German 2nd Army withdrew to the Vistula delta southeast of the city. Evacuations of civilians and military personnel from there and the Hel Peninsula continued until 10 May 1945. The Soviets declared the East Pomeranian offensive complete a week after the fall of Danzig.
The trailer had a fully metallic design, although the wheels remained wooden, as it was drawn by four horses. The Kleinfunkwagen, like many similar trailers, consisted of two sections: the main trailer housing the receiver and most of the equipment, and the rear half containing the transmitter and additional gear
The Danzig�Gotenhafen Fortified Area�also the main port for refugees fleeing East Prussia�was ordered to be defended as long as possible by Saucken to keep evacuation routes open.
Rokossovsky launched his final offensive on 15 March 1945, with the main thrust toward the coast at Zoppot, between Gdingen and Danzig, undertaken by the 70th and 49th Armies advancing in parallel. Fighting was intense, but by 19 March 1945, Soviet spearheads had reached the heights over Zoppot, while the 4th Panzer Division had been pushed back to the outskirts of Danzig itself. By 22 March, the 70th Army reached the sea, splitting the German defense. Gdingen fell on 26 March 1945, with defenders and many civilians retreating to the headland at Oxh�ft, from where they were evacuated to the Hel Peninsula.
Danzig finally fell on 30 March 1945. The remnants of the German 2nd Army withdrew to the Vistula delta southeast of the city. Evacuations of civilians and military personnel from there and the Hel Peninsula continued until 10 May 1945. The Soviets declared the East Pomeranian offensive complete a week after the fall of Danzig.
The trailer had a fully metallic design, although the wheels remained wooden, as it was drawn by four horses. The Kleinfunkwagen, like many similar trailers, consisted of two sections: the main trailer housing the receiver and most of the equipment, and the rear half containing the transmitter and additional gear
Super rare relics with stunning original paintwork still visible! They have been lightly cleaned and treated with Renaissance wax to preserve their condition. Solid and well-preserved, these pieces make a fantastic addition to any collection.
The Danzig�Gotenhafen Fortified Area�also the main port for refugees fleeing East Prussia�was ordered to be defended as long as possible by Saucken to keep evacuation routes open.
Rokossovsky launched his final offensive on 15 March 1945, with the main thrust toward the coast at Zoppot, between Gdingen and Danzig, undertaken by the 70th and 49th Armies advancing in parallel. Fighting was intense, but by 19 March 1945, Soviet spearheads had reached the heights over Zoppot, while the 4th Panzer Division had been pushed back to the outskirts of Danzig itself. By 22 March, the 70th Army reached the sea, splitting the German defense. Gdingen fell on 26 March 1945, with defenders and many civilians retreating to the headland at Oxh�ft, from where they were evacuated to the Hel Peninsula.
Danzig finally fell on 30 March 1945. The remnants of the German 2nd Army withdrew to the Vistula delta southeast of the city. Evacuations of civilians and military personnel from there and the Hel Peninsula continued until 10 May 1945. The Soviets declared the East Pomeranian offensive complete a week after the fall of Danzig.
The trailer had a fully metallic design, although the wheels remained wooden, as it was drawn by four horses. The Kleinfunkwagen, like many similar trailers, consisted of two sections: the main trailer housing the receiver and most of the equipment, and the rear half containing the transmitter and additional gear
The Danzig�Gotenhafen Fortified Area�also the main port for refugees fleeing East Prussia�was ordered to be defended as long as possible by Saucken to keep evacuation routes open.
Rokossovsky launched his final offensive on 15 March 1945, with the main thrust toward the coast at Zoppot, between Gdingen and Danzig, undertaken by the 70th and 49th Armies advancing in parallel. Fighting was intense, but by 19 March 1945, Soviet spearheads had reached the heights over Zoppot, while the 4th Panzer Division had been pushed back to the outskirts of Danzig itself. By 22 March, the 70th Army reached the sea, splitting the German defense. Gdingen fell on 26 March 1945, with defenders and many civilians retreating to the headland at Oxh�ft, from where they were evacuated to the Hel Peninsula.
Danzig finally fell on 30 March 1945. The remnants of the German 2nd Army withdrew to the Vistula delta southeast of the city. Evacuations of civilians and military personnel from there and the Hel Peninsula continued until 10 May 1945. The Soviets declared the East Pomeranian offensive complete a week after the fall of Danzig.
The trailer had a fully metallic design, although the wheels remained wooden, as it was drawn by four horses. The Kleinfunkwagen, like many similar trailers, consisted of two sections: the main trailer housing the receiver and most of the equipment, and the rear half containing the transmitter and additional gear
